Contextual factors play a key role in musculoskeletal disorders. Contextual factors are intrinsically linked to patients’ perception and management of their condition. For example, exercise has been heralded as a fist-line treatment for various MSK disorders but lack understanding of its specific therapeutic effects. Recent studies show that there is a dearth of evidence in support of efficacy when it comes to the intended therapeutic element(s) of the intervention of exercise. (1) Contextual factors have been reported to make up about 75% of the total observed improvement for a wide range of therapies (1) (2) commonly used in the management of MSK disorders.
Given the importance of contextual factors in MSK disorders, clinicians need to be aware of individual factors that influence a patient’s pain experience. In order to achieve that goal, a patient needs to be understood as a person in all its complexity. Effective patient-centered consultations are required in order to build trust and alliance between the patient and the clinician to achieve that understanding. In turn, patient-centered, collaborative management yields better outcomes. (3)
Effective and reassuring consultations include good data collection, relationship building, avoiding generic reassurance, exchanging information (cognitive reassurance), and provision of validation. (4)
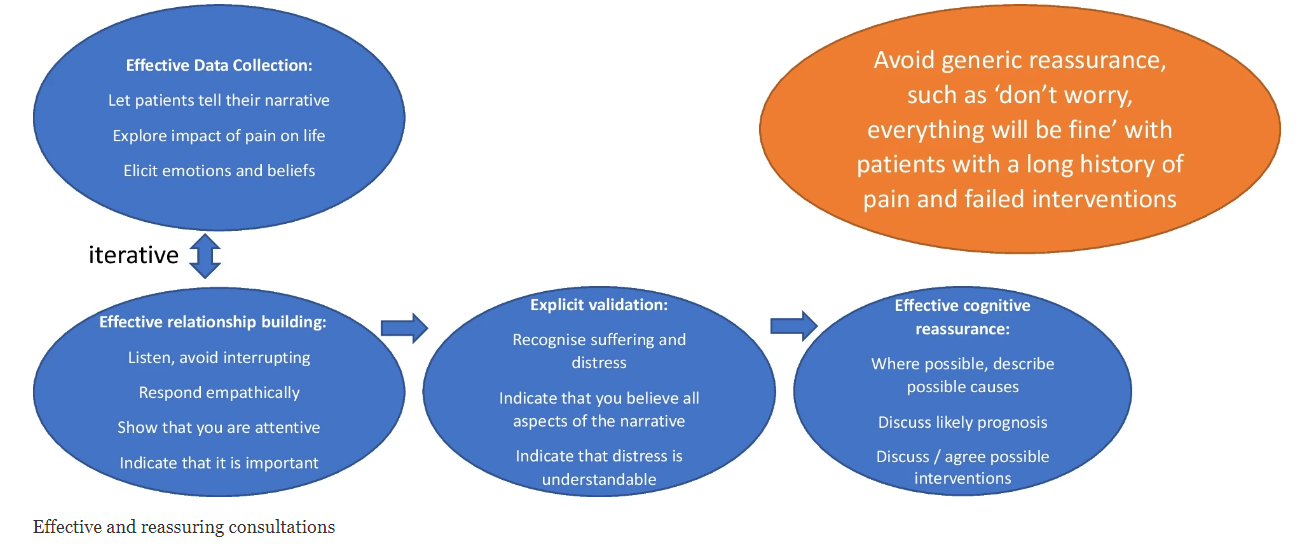
Application in practice include asking open-ended questions, let patients tell their story, acknowledging patient’s experiences, avoiding medical jargon, and agree on ways forward. (3) (4)
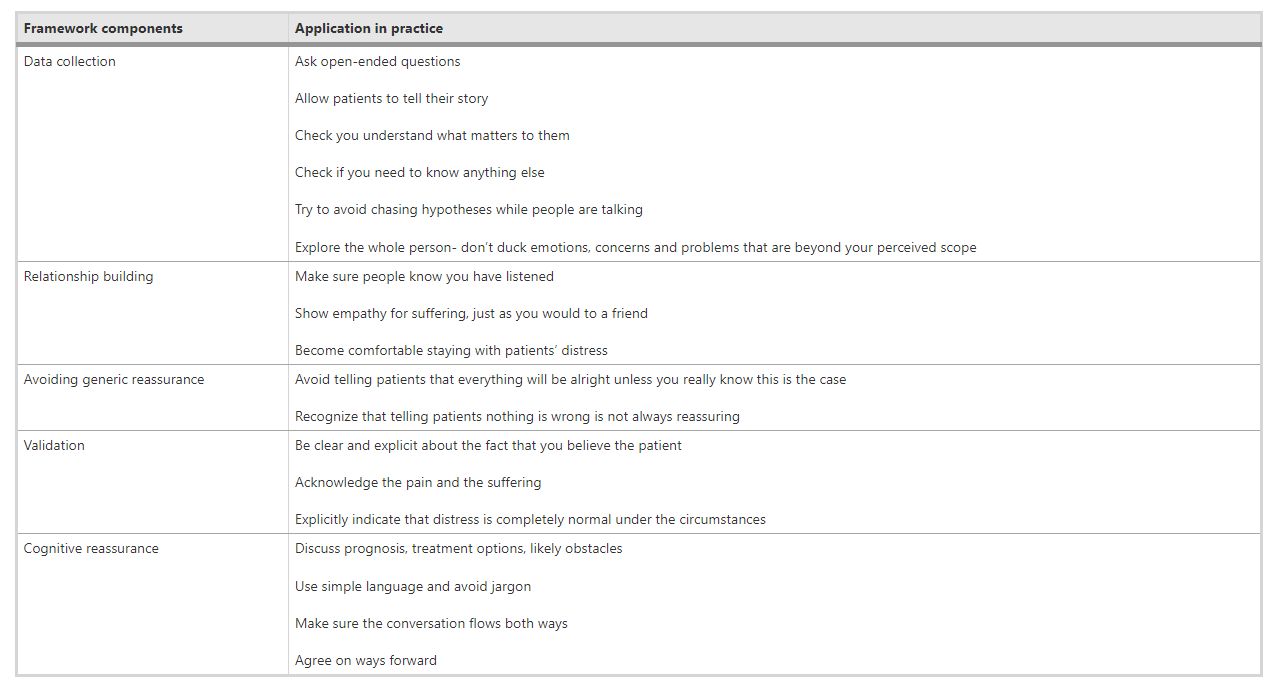
Clinicians need to develop their skills in patient-centered communication and develop therapeutic collaboration with patients to achieve meaningful results. The literature clearly shows that better therapeutic outcomes are achieved that way. (3)


